
|
MiCOM P632
Checking Differential
Protection
|

|
MiCOM P632
Checking Differential
Protection
|
For single-side feed, the fault current characteristic crosses the first knee of the tripping characteristic of the P632 so that the basic threshold value is always checked.
The current I to which the P632 responds for single-side feed is calculated as follows:
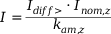
| ▪ |
z: transformer end (a, b) |
| ▪ |
Idiff>: set operate value |
| ▪ |
Inom,z: nominal current of the P632 for transformer end a, b |
| ▪ |
kam,z: amplitude-matching factor of transformer end a, b |
For single-side one-phase or two-phase feed, a vector group-matching factor in accordance with the set vector group ID needs to be taken into account in addition to the amplitude-matching factor. The vector group-matching factors are given in the tables below and the threshold current is calculated as follows:
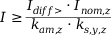
| ▪ |
z: transformer end (a, b) |
| ▪ |
Idiff>: set operate value |
| ▪ |
Inom,z: nominal current of the P632 for transformer end a, b |
| ▪ |
kam,z: amplitude-matching factor of transformer end a, b |
| ▪ |
ks,y,z: vector group-matching factor (see tables below) |
The differential and restraining currents formed by the P632 are displayed as measured operating data. They aid in assessing whether the connection of the P632 to the system current transformers and the setting of the vector group ID are correct. The tables below give the factors ks which serve to calculate the differential current for single-side feed. The display of differential and restraining currents is prevented, however, if they fall below minimum thresholds that can be set by the user.
Id,y = kam,z·ks,y,z·Itest,x
| ▪ |
x: phase A, B or C |
| ▪ |
z: transformer end (a, b) |
| ▪ |
measuring system 1, 2 or 3 |
| ▪ |
Id,y: differential current as displayed |
| ▪ |
kam,z: amplitude-matching factor of transformer end a, b |
| ▪ |
ks,y,z: vector group-matching factor (see tables below) |
| ▪ |
Itest,x: test current phase A, B or C |
In evaluating the test results, one should be aware that the P632 will trip as follows, if a value of Idiff>> or Idiff>>> is exceeded.
| ▪ |
Idiff>> exceeded: Trip regardless of the inrush and overfluxing restraint; |
| ▪ |
Idiff>>> exceeded: Trip regardless of the restraining current and regardless of all other restraints. |
|
Transformer end |
a |
b | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vector group ID |
|
0=12 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 1 |
0.67 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 2 |
0.33 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 3 |
0.33 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.58 |
0.67 |
0.58 |
0.33 |
0.00 |
Tab. 10-1: Factors for single-side, one-phase feed in phase A, zero sequence-filtered.
|
Transformer end |
a |
b | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vector group ID |
|
0=12 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 1 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 2 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 3 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
1.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
1.00 |
1.15 |
Tab. 10-2: Factors for single-side, two-phase, phase-opposition feed in phases B to C, zero sequence-filtered.
|
Transformer end |
a |
b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vector group ID |
|
0=12 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 1 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 2 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 3 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
Tab. 10-3: Factors for single-side, one-phase feed in phase A, not zero sequence-filtered.
|
Transformer end |
a |
b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vector group ID |
|
0=12 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 1 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 2 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
|
DIFF: Diff. current 3 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
1.00 |
Tab. 10-4: Factors for single-side, two-phase, phase-opposition feed in phases B to C, not zero sequence-filtered.
The connection of the phase currents can be checked using the phase angles provided as measured operating data by the P632.
If the phase currents are connected correctly and there is an ideal balanced load on the transformer, the phase angles between the phase currents of any one transformer end are displayed as follows:
| ▪ |
φAB,z = φBC,z = φCA,z = 120° |
| ▪ |
φAB,z = φBC,z = φCA,z = −120° |
This is not influenced by the set value of the function parameter for the phase sequence.
The phase angle between the phase currents of two transformer ends for a particular phase is a function of the vector group of the transformer. This phase angle should be displayed as follows:
|
Vector group |
|
|---|---|
|
0 = 12 |
φx,A–z = ±180° |
|
1 |
φx,A–z = −150° |
|
2 |
φx,A–z = −120° |
|
3 |
φx,A–z = −90° |
|
4 |
φx,A–z = −60° |
|
5 |
φx,A–z = −30° |
|
6 |
φx,A–z = 0° |
|
7 |
φx,A–z = 30° |
|
8 |
φx,A–z = 60° |
|
9 |
φx,A–z = 90° |
|
10 |
φx,A–z = 120° |
|
11 |
φx,A–z = 150° |
This is not influenced by the set value of the function parameter for the phase sequence. Changing the setting for the connection scheme of an involved series transformer, on the other hand, will change the measured operating data value by ±180°.