
|
MiCOM P632
Zero-sequence Current
Filtering
|

|
MiCOM P632
Zero-sequence Current
Filtering
|
Tab. 3-1: “Required operations for vector groups with or without zero-sequence current filtering” shows that the zero-sequence current is subtracted from the phase currents of winding a and, for all even vector groups, from the phase currents of winding b. According to the theory of symmetric components, the zero-sequence current is calculated as follows:
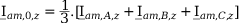
z: end a or b
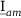 : amplitude-matched current
: amplitude-matched current
Zero-sequence filtering may be disabled separately for each end.
In general this disabling of zero-sequence filtering is intended for even-numbered vector groups. Should the side considered here require the setting of an odd-numbered vector group while at the same time no operational system star point grounding is provided within the protected area, then, in view of increased sensitivity with single-pole internal faults, it is recommended that the respective zero-sequence current is fed to the individual measuring systems again.
Zero-sequence filtering for the transformer ends a or b is enabled using the setting parameters:
| ▪ |
DIFF: 0-seq. filt.a en.PSx |
| ▪ |
DIFF: 0-seq. filt.b en.PSx |
Tab. 3-1: “Required operations for vector groups with or without zero-sequence current filtering” lists the required operations for all vector groups that may occur. The indices in the equations have the following meanings:
am: amplitude-matched
x: phase A, B or C
x+1: cyclically trailing phase
x-1: cyclically leading phase
|
End |
ID of the vector group |
Setting: With zero-sequence filtering |
Setting: Without zero-sequence filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
|
a |
|
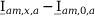 |
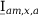 |
|
b |
0=12 |
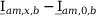 |
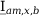 |
|
1 |
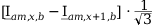 |
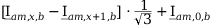 | |
|
2 |
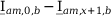 |
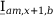 | |
|
3 |
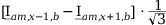 |
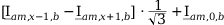 | |
|
4 |
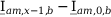 |
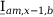 | |
|
5 |
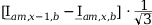 |
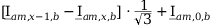 | |
|
6 |
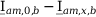 |
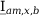 | |
|
7 |
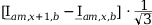 |
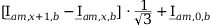 | |
|
8 |
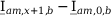 |
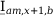 | |
|
9 |
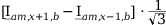 |
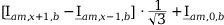 | |
|
10 |
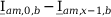 |
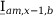 | |
|
11 |
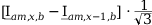 |
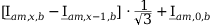 |
Tab. 3-1: Required operations for vector groups with or without zero-sequence current filtering
Vector group matching is via a straight-forward input of the vector group identification number provided that the phase currents of the high and low voltage side(s) are connected in standard configuration (see section Chapter “Conditioning of the Measured Values”). For other configurations, special considerations apply (see Chapter “Settings”). A reverse phase rotation (A-C-B) needs to be taken into account by making the appropriate setting at the P632. The P632 will then automatically form the complementary value of the set vector group ID to the number 12 (vector group ID = 12 – set ID).