
|
MiCOM P632
Tripping Characteristics
|

|
MiCOM P632
Tripping Characteristics
|
The differential and restraining current values for each measurement system are calculated from the current values after amplitude and vector group matching. The following equations are valid for uniformly defined current arrows relative to the protected equipment, e.g. all the current arrows of all windings point either towards the protected object or away from it.
Calculation of differential and restraining currents:
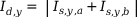
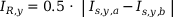
The tripping characteristic of the P632 line differential protection device has two knee points. The first knee-point depends on the setting at DIFF: Idiff> PSx and is on the intersection with the tripping characteristic for single-side feed.
If the current transformer supervision (CTS) function is used, the basic pick-up sensitivity DIFF: Idiff> PSx can be increased to a set value (DIFF: Idiff>(CTS) PSx) when a CT fault is detected. See details given in the section describing the CTS function group.
The second knee of the tripping characteristic is defined by the setting at DIFF: Idiff> PSx.
The characteristic equations for the three different ranges are given below. Fig. 3-96 shows the tripping characteristic.
Characteristics equation for the range 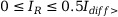 :
:
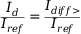
Characteristics equation for the range 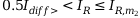 :
:
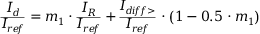
Characteristics equation for the range 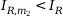 :
:
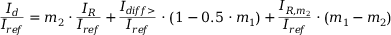
Iref: reference current
m1: gradient of the characteristic in range 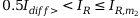
m2: gradient of characteristic in range 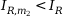
If the current transformer supervision (CTS) function is used, the basic pick-up sensitivity DIFF: Idiff> PSx can be increased to a value set at DIFF: Idiff>(CTS) PSx.